Chronometer vs Chronograph: What's the Difference?
Wondering about the difference between a chronometer and a chronograph? While they may sound similar, these two types of timepieces serve unique purposes in the world of horology.
What Is a Chronometer?
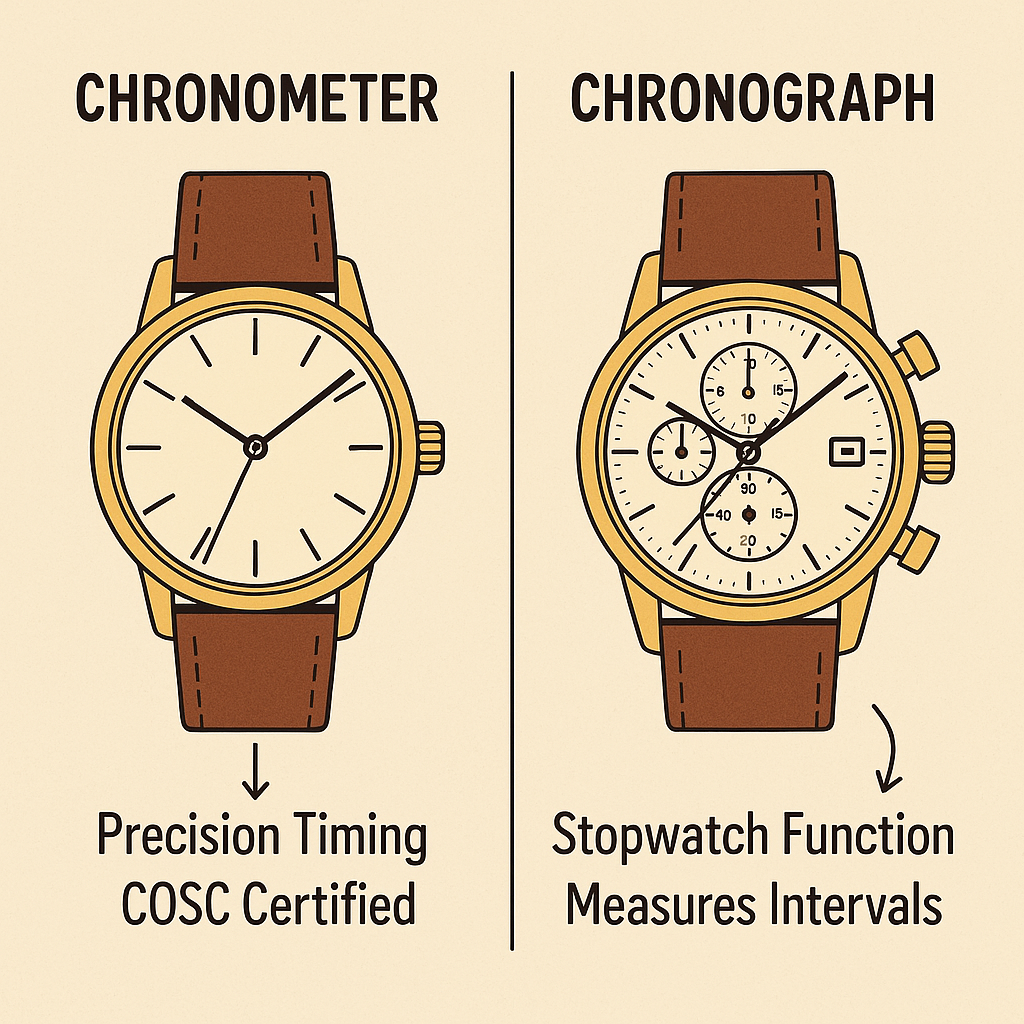
A chronometer is a high-precision watch that has passed official testing for accuracy, often certified by institutes like COSC (Contrôle Officiel Suisse des Chronomètres). These watches are known for their timekeeping reliability and are used by professionals such as sailors, pilots, and scientists.
What Is a Chronograph?
A chronograph is a multifunctional watch that includes a built-in stopwatch. It features pushers and sub-dials to measure elapsed time, making it a favorite among athletes, racers, and aviation enthusiasts.
Chronometer vs Chronograph: Key Differences
| Feature |
Chronometer |
Chronograph |
| Purpose |
High-accuracy timekeeping |
Stopwatch and time tracking |
| Certification |
Yes (COSC certified) |
No (unless also a chronometer) |
| Main Function |
Precision timing |
Measuring intervals |
| Design |
Clean, classic face |
Multi-dial interface |
| Best For |
Pilots, divers, professionals |
Athletes, racers, casual users |
Which One Should You Choose?
Choose a chronometer if accuracy and certification are your top priorities. Prefer a watch with stopwatch capabilities? Then a chronograph is perfect for you. Many modern timepieces combine both, giving you the best of both worlds.
Did You Know?
Some high-end brands like Omega and Breitling produce chronographs that are also COSC-certified chronometers.
The term "chronograph" comes from the Greek words "chrono" (time) and "graph" (writing), originally referring to mechanical devices that recorded time on paper.
Quartz vs Mechanical Watches: Which One Is Better?
When choosing a watch, many people ask: should I get a quartz or a mechanical movement? Both have strengths, and your choice depends on what you value most — precision, tradition, or convenience.
What Is a Quartz Watch?
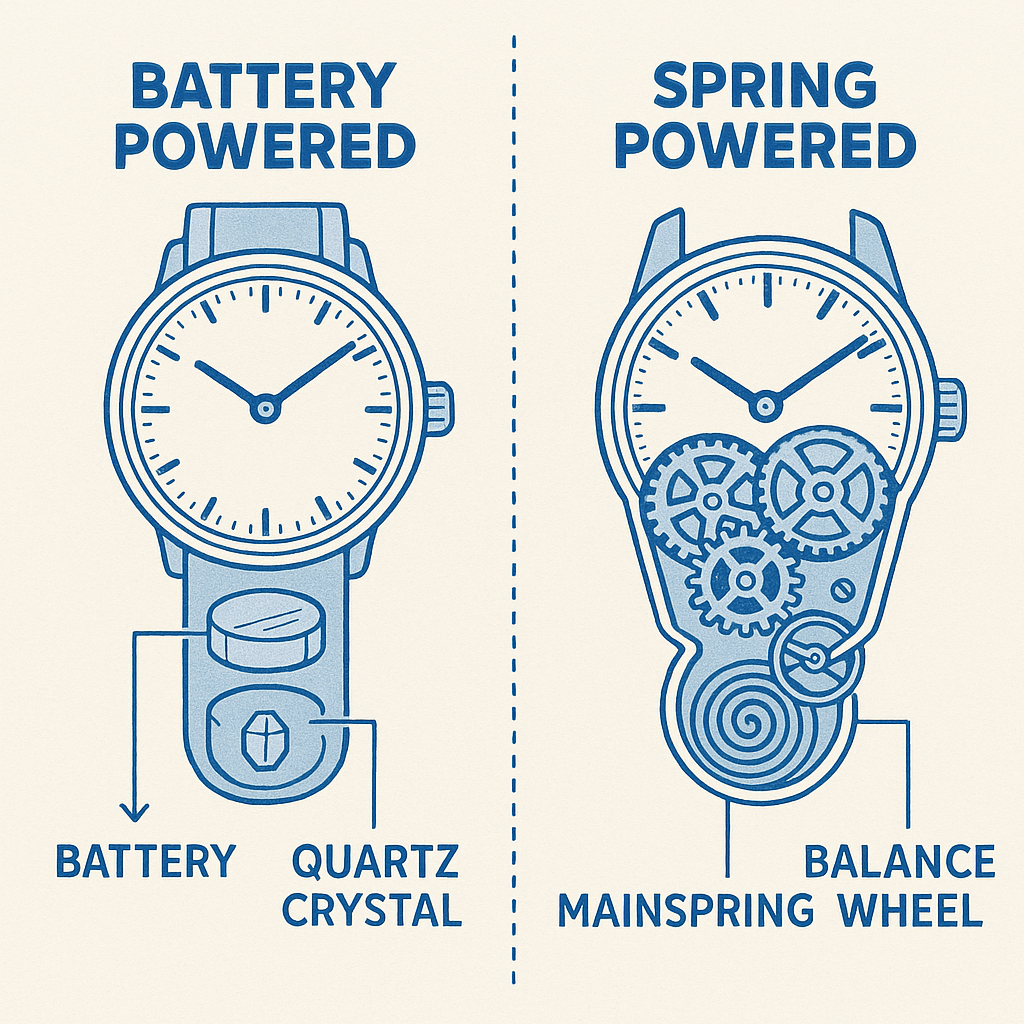
A quartz watch uses a battery-powered electronic oscillator regulated by a quartz crystal to keep time. These watches are incredibly accurate and require minimal maintenance.
What Is a Mechanical Watch?
A mechanical watch is powered by a wound spring (mainspring) and relies on intricate gears and components. It can be either manual or automatic and is appreciated for its craftsmanship and heritage.
Quartz vs Mechanical: Key Differences
| Feature |
Quartz |
Mechanical |
| Power Source |
Battery |
Wound spring |
| Accuracy |
Very high (±15 sec/month) |
Moderate (±5 sec/day) |
| Maintenance |
Low |
Higher (requires servicing) |
| Movement Type |
Electronic |
Mechanical (manual or automatic) |
| Price Range |
Affordable to mid-range |
Mid to luxury |
Which One Should You Choose?
If you want precision, affordability, and ease of use, a quartz watch is ideal. If you value tradition, craftsmanship, and enjoy the mechanical aspect of watches, go for a mechanical timepiece.
Automatic vs Manual Watches: What's the Difference?
Both automatic and manual watches are types of mechanical timepieces, meaning they don't require batteries. But the way they're powered and maintained is different — and that difference matters depending on how you wear your watch.
What Is a Manual Watch?
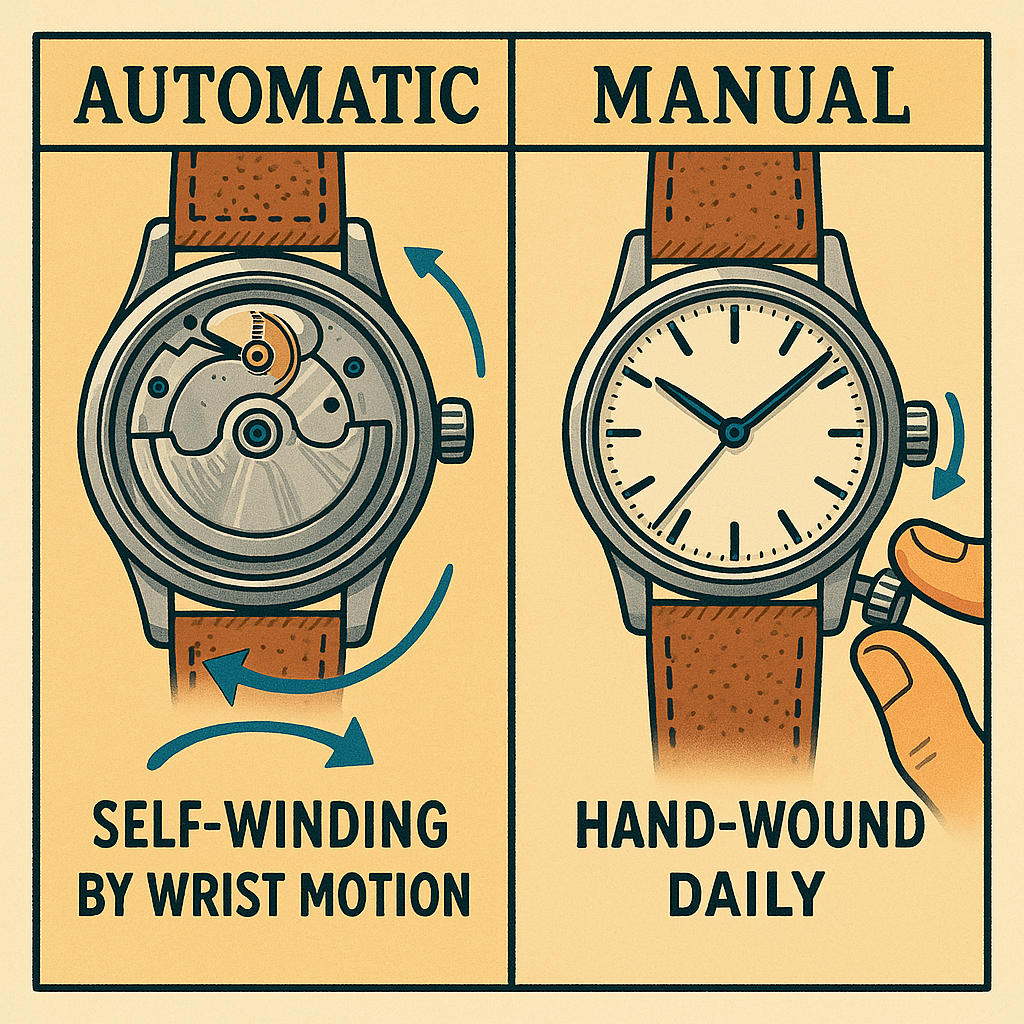
A manual watch, also called a hand-wound watch, must be wound regularly by turning the crown. It's a traditional choice loved by collectors who enjoy the ritual and connection to the mechanics.
What Is an Automatic Watch?
An automatic watch winds itself using a rotor that moves with your wrist. As long as you wear it regularly, it keeps ticking — no winding required.
Automatic vs Manual: Key Differences
| Feature |
Manual |
Automatic |
| Winding |
Manual (via crown) |
Self-winding (via wrist movement) |
| Power Reserve |
Usually 24–48 hours |
Usually 36–72 hours |
| Maintenance |
Requires daily winding |
Low if worn regularly |
| Complexity |
Simpler movement |
More moving parts |
| User Experience |
More hands-on |
More convenient |
Which One Should You Choose?
If you enjoy interacting with your watch and don't mind daily winding, a manual watch offers a charming, traditional experience. For hassle-free timekeeping, an automatic watch is the perfect blend of engineering and convenience.
Chronometer History
The Evolution of Timekeeping
The journey of chronometers began in the 18th century with marine chronometers, revolutionizing navigation at sea. These precision instruments were crucial for determining longitude, marking a significant milestone in the history of timekeeping.
The Quartz Revolution
The introduction of quartz technology in the 20th century transformed timekeeping forever. Quartz chronometers offered unprecedented accuracy, making precise time measurement accessible to the masses.
Modern Timekeeping
Today's chronometers combine centuries of innovation with cutting-edge technology, from atomic clocks to smartwatches, continuing the legacy of precise time measurement.